| Name : US History to 1877 Science Review checklist Part One | |||||
| Put a check in the box each time you answer the question correctly | Cover the right column with a piece of paper or your hand. Answer the question and check your answer. Each time you answer correctly, put a check in the little box. By test time, you'll want a check in each of the boxes. |
Cover these answers! |
|||
| 1. How many continents are there? | Seven | ||||
| 2. The land mass that includes both Europe and Asia is called: | Eurasia | ||||
3.
Name the eight geographic regions of North
America.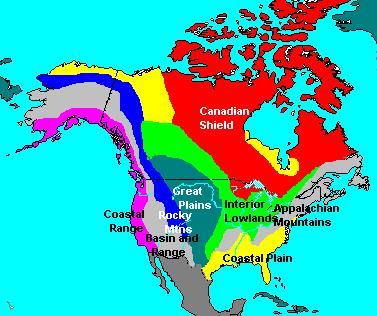 |
Coastal Plain, Appalachian Mountains, Canadian Shield, Interior Lowlands, Great Plains, Rocky Mountains, Basin and Range, and Coastal Range. | ||||
|
4.
Name the geographic region described: • Located along the Atlantic Ocean and Gulf of Mexico • Broad lowland providing many excellent harbors |
Coastal Plain | ||||
|
5.
Name the geographic region described: • Located west of Coastal Plain extending from eastern Canada to western Alabama • Old, eroded mountains (oldest mountain range in North America) |
Appalachian Mountains | ||||
|
6.
Name the geographic region described: • Wrapped around Hudson Bay in a horseshoe shape • Hills worn by erosion and hundreds of lakes carved by glaciers • Holds some of the oldest rock formations in North America |
Canadian Shield | ||||
|
7.Name
the geographic region described: • Located west of the Appalachian Mountains and east of the Great Plains • Rolling flatlands with many rivers, broad river valleys, and grassy hills |
Interior Lowlands | ||||
|
8.
Name the geographic region described: • Located west of Interior Lowlands and east of the Rocky Mountains • Flat land that gradually increases in elevation westward; grasslands |
Great Plains | ||||
|
9.
Name the geographic region described: • Located west of the Great Plains and east of the Basin and Range • Rugged mountains stretching from Alaska to Mexico; high elevations • Contains the Continental Divide, which determines the directional flow of rivers |
Rocky Mountains | ||||
|
10.
Name the geographic region described: • Located west of Rocky Mountains and east of the Sierra Nevadas and the Cascades • some small mountain ranges and Death Valley, the lowest point in North America |
Basin and Range | ||||
|
11.
Name the geographic region described: • Rugged mountains along the Pacific Coast that stretch from California to Canada • Fertile valleys |
Coastal Range | ||||
12.This
ocean served as the highway for explorers, early settlers, and later
immigrants.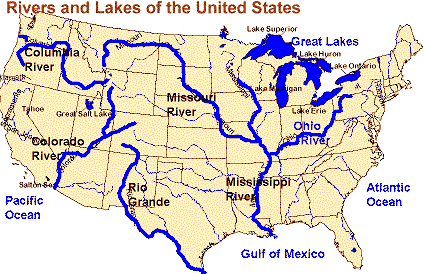 |
The Atlantic Ocean | ||||
| 13. This river was the gateway to the west. | The Ohio River | ||||
| 14. Inland port cities grew in the Midwest along these lakes. | The Great Lakes | ||||
| 15. These rivers were the transportation arteries for farm and industrial products. They were links to ports and other parts of the world. | The Mississippi and Missouri Rivers | ||||
| 16. This river was explored by Lewis and Clark. | The Columbia River | ||||
| 17. This river was explored by the Spanish. | The Colorado River | ||||
| 18. This river forms the border with Mexico. | The Rio Grande | ||||
| 19. This body of water provided the French and Spanish with exploration routes to Mexico and other parts of America | The Gulf of Mexico | ||||
20.
These American Indians lived in present-day
Alaska and northern Canada. They lived in Arctic areas where the
temperature is below freezing much of the year.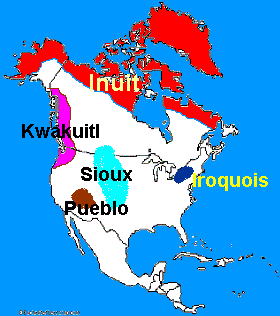 |
Inuit | ||||
| 21. These Indians lived in the Pacific Northwest coast, where the climate was rainy and mild. | Kwakiutl | ||||
| 22. These Indians lived on the Great Plains. This region, which is covered by dry grasslands, is in the interior part of the United States. | Sioux | ||||
| 23. These Indians lived in the Southwest in present-day New Mexico and Arizona, where they lived in desert areas and areas bordering cliffs and mountains | Pueblo | ||||
| 24. These Indians lived in the heavily forested Eastern Woodland in the Northeast. | Iroquois | ||||
| 25. What factors greatly affected the way each of the American Indian groups lived, found food, and built shelters? | Geography and climate | ||||
| 26. What did Iroquois Indians of the Eastern Woodland use to build their homes? | Wood from the forests. | ||||
| 27. Which Indian group lived in teepees made from buffalo skin? | Sioux | ||||
| 28. Why did European countries compete for power in North America? |
Reasons for exploration • Economic—Gold, natural resources, and trade • Religious—Spread of Christianity • Competitions for empire and belief in superiority of own culture |
||||
| 29. What were the obstacles faced by the explorers? |
• Poor maps and navigational tools • Disease/starvation • Fear of unknown • Lack of supplies |
||||
30.
What were the accomplishments of the
explorations?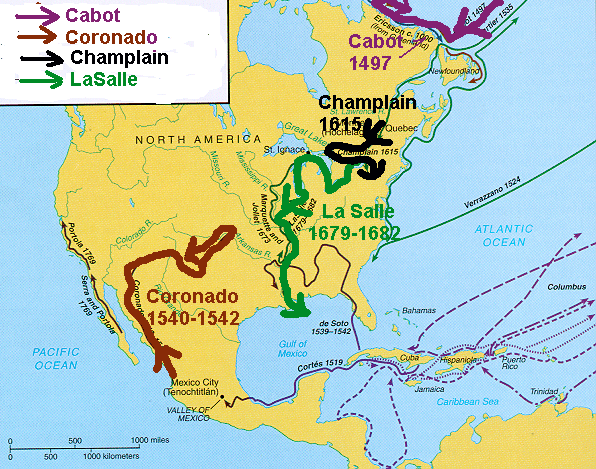 |
• Exchanged goods and ideas • Improved navigational tools and ships • Claimed territories |
||||
| 31. What regions of North America were explored and settled by France? |
-Samuel de Champlain established the French
settlement of Quebec. -Robert La Salle claimed the Mississippi River Valley |
||||
| 32. What regions of North America were explored and settled by Spain? | Francisco Coronado claimed southwest United States for Spain. | ||||
| 33. What regions of North America were explored and settled by England? | One of the first explorers sent by England was John Cabot. He explored eastern Canada. Later, various groups from England settled the 13 colonies. | ||||
| 34. Who claimed the Mississippi River Valley for France? | Robert La Salle | ||||
| 35. Who explored eastern Canada for England? | John Cabot | ||||
| 36. Who established the French settlement of Quebec (Canada)? | Samuel de Champlain | ||||
| 37. Who claimed land in the southwest for Spain? | Francisco Coronado | ||||
| 38. What regions of the world were explored by Portugal? | The Portuguese explored and traded in West Africa. | ||||
| 39. How did the American Indians and the Spanish interact with each other? |
The Spanish – Conquered and enslaved American Indians – Brought Christianity to the New World – Brought European diseases |
||||
| 40. How did the American Indians and the French interact with each other? |
The French – Established trading posts – Spread Christian religion (the French did not enslave Indians or take their land) |
||||
| 41. How did the American Indians and the English interact with each other? |
The English – Established settlements and claimed ownership of land – Learned farming techniques from American Indians – Traded |
||||
| 42. In what areas did the Europeans and Indians sometimes cooperate? |
• Sharing of technologies like weapons and
farm tools • Trade • English learned farming techniques and learned about new crops. |
||||
| 43. What were some of the areas of conflict between the American Indians and the Europeans? |
Areas of conflict • Land, Land, Land • Competition for trade • Differences in cultures • Disease • Language difference |
||||
| 44.Name the three West African societies that became powerful by controlling trade in West Africa. | Ghana, Mali, and Songhai | ||||
| 45. Where were the empires of Ghana, Mali, and Songhai were located? | West Africa | ||||
| 46. The _______ carried goods from Europe to West African empires. | Portuguese | ||||
| 47. What goods did the Portuguese trade with the West African empires? | The Portuguese traded metals, cloth, and other manufactured goods for West African gold. | ||||
| 48. Colonies in North America were established for ______ and ______ reasons | religious and economic | ||||
| 49. Roanoke Island (Lost Colony) was established as an ______ venture (for money and profit). | economic | ||||
| 50. Jamestown was an _______ venture by the Virginia Company of London (for profit). | economic | ||||
| 51. Plymouth colony was settled by Pilgrim separatists from the Church of England who wanted to avoid ____________. | religious persecution | ||||
| 52. Massachusetts Bay Colony was settled by _____ who wanted to avoid religious persecution. | Puritans | ||||
| 53. Pennsylvania was settled by the ____________, who wanted to have freedom to practice their faith without interference. | Quakers | ||||
| 54. Georgia was settled by people who had been in _______ in England. They wanted a new life and ______ freedom in the New World. | debtor’s prison; economic | ||||
| 55. Which colony was the first permanent English settlement in North America? | Jamestown (1607) | ||||
| 56. Which colony was the "lost colony"? | Roanoke Island | ||||
| 57. Where did the Quakers settle? | Pennsylvania | ||||
| 58. Name three colonies that were settled for economic reasons? | Roanoke Island, Jamestown, and Georgia | ||||
| 59. Name three colonies that were settled for religious reasons. | Massachusetts Bay, Plymouth, and Pennsylvania | ||||
| 60.Name the four New England colonies. | New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut | ||||
| 61. Name the four Mid-Atlantic colonies | New Jersey, Delaware, Pennsylvania, New York | ||||
| 62. Name the five Southern colonies | Virginia, Maryland, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia | ||||
|
63. Which group of colonies is
described below? Excellent harbors made trade the chief source of income. Fishing, shipbuilding, naval supplies and lumber were also important. |
New England colonies | ||||
|
64.
Which group of colonies is described below? These colonies had a diverse population, including Quakers, Scots-Irish, Germans, Dutch, Swedes, and immigrants from many other European countries. |
Mid- Atlantic colonies | ||||
|
65. Which group of colonies is
described below? A warm climate, long growing season and fertile lands produced rich crops of cotton, tobacco, rice and indigo. |
The Southern colonies | ||||
|
66.
Which group of colonies is described below? Colonists lived in or around villages and towns. Citizens met in town meetings to discuss the important issues of the day. |
New England colonies | ||||
|
67.
Which group of colonies is described below? Few cities, few schools. Social life centered around the plantations. |
Southern colonies | ||||
|
68.
Which group of colonies is described below?
A mix of thriving cities, and successful farms. Philadelphia was one of the most important cities in colonial America. Shopping was done in market towns. |
Mid- Atlantic colonies | ||||
|
69.
Which group of colonies is described below? Most of the early settlers lived in towns and villages around the excellent harbors. Many carried on some kind of trade or business. |
New England colonies | ||||
|
70.
Which group of colonies is described below? Small farms surrounded the towns and villages, but the rocky, thin soil made it difficult to make a living from farming. |
New England colonies | ||||
|
71.
Which group of colonies is described below?
Mostly rural (farming). A mix of large plantations supported by slave labor and smaller farms. |
Southern colonies | ||||
|
72.
Which group of colonies is described below?
Society here was more tolerant than elsewhere and accepted a mix of people, languages, religions and cultures. |
Mid-Atlantic colonies | ||||
|
73.
Which group of colonies is described below?
These colonies grew wealthy from exports of tobacco, rice and indigo (a blue dye used in coloring fabrics) |
Southern colonies | ||||
| 74. These people worked as craftsmen in towns and on plantations. | Artisans | ||||
| 75. These people worked as caretakers, house-workers, homemakers. They could not vote and had few chances for an education. | Women | ||||
| 76. These people were men and women who did not have money for passage to the colonies and who agreed to work without pay for the person who paid for their passage. They were free at the end of their contract. | Indentured servants | ||||
| 77. These people were captured in their native Africa and sold to slave traders, then were shipped to the colonies where they were sold. | Slaves | ||||
| 78. Slaves were owned as _______ for life. They had no ______. |
property; rights |
||||
| 79.How did England impose economic control over the colonies? |
• England imposed strict control over
trade. • England taxed the colonies after the French and Indian War. • Colonies traded raw materials for goods. |
||||
| 80. How did England impose political control over the colonies? |
• Colonists had to obey English laws that
were enforced by governors. • Colonial governors were appointed by the king or by the proprietor. • Colonial legislatures made laws for each colony and were monitored by colonial governors |
||||
| 81. Why did England impose taxes such as the Stamp Act after the French and Indian War? |
To raise revenue to pay the cost of the
French and Indian War. · To help with the maintaining of English troops in the colonies |
||||
| 82. Who enforced English laws in the colonies? | The colonial governors, who were generally appointed by the English King or proprietor | ||||
| 83.Were colonial legislatures (law-making bodies) free to make laws for the colonies? | No, colonial legislatures were monitored by the colonial governors who were appointed by England | ||||
| 84. Why did colonists feel that taxes like the Stamp Act were unfair? | Because colonies had no representation in Parliament. | ||||
| 85. Why were the colonists becoming increasingly unhappy with England? |
1. Colonies had no representation in
Parliament. 2. Some colonists resented power of colonial governors. 3. England wanted strict control over colonial legislatures. 4. Colonies opposed taxes. 5. The Proclamation of l763 hindered the western movement of settlers |
||||
| 86. Why did the Proclamation of l763 anger the colonists? | It did not permit them to move west of the Appalachian Mountains in search of better farmland and new opportunities. | ||||
| 87. Why did England impose the Proclamation of 1763? | England did not want to spend money protecting and defending settlers as they moved west onto new lands. | ||||
| 88. Why did England want to increase control over the colonies? |
• England desired to remain a world power. • England needed to raise money to pay the cost of the French and Indian War and felt it was necessary to impose taxes such as the Stamp Act |
||||
| 89. As England expanded control over the American colonies, many colonists became: | dissatisfied and rebellious | ||||
| 90. This English philosopher's ideas about government helped shape the thinking of revolutionary leaders. | John Locke | ||||
| 91. What were some of John Locke's ideas? |
· People have natural rights to life,
liberty, and property. · Government is created to protect the rights of people and has only the limited and specific powers the people consent to give it. |
||||
| 92. John Locke's ideas about government were expressed in the: | Declaration of Independence | ||||
| 93. Who wrote the Declaration of Independence? | Thomas Jefferson | ||||
| 94. What ideas about government were expressed in the Declaration of Independence? |
• People have “certain unalienable rights”
(rights that cannot be taken away)—life, liberty, pursuit of happiness. • People establish government to protect those rights. • Government derives power from the people. • People have a right and a duty to change a government that violates their rights. |
||||
| 95. What are unalienable rights? | Rights that cannot be taken away (life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness). | ||||
| 96. Jefferson wrote in the Declaration of Independence that the right to "life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness" are: | unalienable rights - in other words rights that cannot be taken away from people | ||||
| 97. An important idea in the Declaration of Independence is that people establish governments to: | protect their rights | ||||
| 98. Jefferson wrote in the Declaration of Independence that government derives (gets) power from: | the people | ||||
| 99. Jefferson wrote in the Declaration of Independence that if the government violates the rights of the people, then people have a right and a duty to: | change the government | ||||
| 100. Who was the British king during the Revolutionary era? | King George III | ||||
| 101. Who was the British general who surrendered at Yorktown? | Lord Cornwallis | ||||
| 102. Who was the Commander of the Continental Army? | George Washington | ||||
| 103. Who was an outspoken member of the House of Burgesses who inspired colonial patriotism with his “Give me liberty or give me death” speech? | Patrick Henry | ||||
| 104. Who was a journalist, and the author of Common Sense? | Thomas Paine | ||||
| 105. Who was a prominent member of Continental Congress who helped frame the Declaration of Independence? | Benjamin Franklin | ||||
| 106.Who was a former slave who wrote poems and plays supporting American independence? | Phyllis Wheatley | ||||
| 107. Who was a patriot who made a daring ride to warn colonists of British arrival, crying, “The British are coming!”? | Paul Revere | ||||
| 108. During the ___________, colonists in Boston were shot after taunting British soldiers. | Boston Massacre | ||||
| 109. Why did Samuel Adams and Paul Revere lead patriots in throwing tea into Boston Harbor during the Boston Tea Party? | to protest tea taxes | ||||
| 110. Delegates from all colonies met to discuss problems with England and to promote independence. This meeting was called the: | First Continental Congress | ||||
| 111. The first battle of the Revolutionary War was the: | Battle of Lexington and Concord | ||||
| 112. Colonies signed the of the Declaration of Independence and declared independence from England on: | July 4, 1776 | ||||
| 113. This American victory was the turning point in the Revolutionary War. | the Battle of Saratoga | ||||
| 114. This was the colonial victory over forces of Lord Cornwallis that marked the end of the Revolutionary War. | Surrender at Yorktown | ||||
| 115. England recognized American independence in this treaty. | The Treaty of Paris | ||||
| 116. What advantages helped the American colonists win the Revolutionary War? |
• Colonists’ defense of their own land,
principles, and beliefs • Support from France and Spain • Strong leadership |
||||
| 117. A constitution written during the Revolution to establish the powers of the new national government was called: | The Articles of Confederation | ||||
| 118. What were the basic weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation? |
• Provided for a weak national government
• Gave Congress no power to tax or regulate commerce among the states • Provided for no common currency • Gave each state one vote regardless of size • Provided for no executive or judicial branch |
||||
| 119. What kind of system of government did the Constitution establish?. |
A federal system of government |
||||
| 110. What is a federal system of government? | A system that divides powers between the national government and the governments of the states | ||||
| 111. What are some of the basic principals of our government? |
Separation of powers Checks and balances |
||||
| 112. The structure of the new national government was based on James Madison’s ___ ___ which called for three separate branches of government. | Virginia Plan | ||||
| 113. What are the three separate branches of government? |
– Legislative Branch – Judicial Branch – Executive Branch |
||||
| 114. What is the job of the Legislative Branch? | to make laws | ||||
| 115. What is the job of the Executive Branch? | to carry out laws | ||||
| 116. What is the job of the Judicial Branch? | to determine if laws are constitutional | ||||
| 117. The legislative branch of the federal government is: | Congress | ||||
| 118.Congress is a two-house legislature consisting of: | the Senate and the House of Representatives | ||||
| 119. All states are represented equally in the: | Senate | ||||
| 120. How many Senators are there per state in the Senate? | 2 | ||||
| 121. In the House of Representatives, the number of each state's representatives is based on: | the state's population | ||||
| 122. Which branch of government is the Supreme Court part of? | The Judicial Branch | ||||
| 123. The head of the Executive Branch is: | The President | ||||
| 124. What is the branch of government that determines if laws made by Congress are constitutional and if laws are being broken? | The Judicial Branch | ||||
| 125. Which branch of government carries out laws? | The Executive Branch | ||||
| 126. The structure of the new national government was based on James Madison’s “Virginia Plan.” What idea did the Virginia Plan contribute? | The idea of 3 separate branches of government. | ||||
| 127. Who wrote the Virginia Plan? | James Madison | ||||
| 128. Another principal of our new government was: | checks and balances | ||||
| 129. What are "checks and balances"? |
• Each branch of government can check the
power of the other. • These checks keep any one branch from gaining too much power. |
||||
| 130. The first ten amendments to the Constitution is the: | Bill of Rights | ||||
| 131. Who was the author of the Bill of Rights? | James Madison | ||||
| 132. What does the Bill of Rights do? | It provides a written guarantee of individual rights | ||||
| 133. What are some of the individual rights guaranteed in the Bill of Rights? | freedom of speech, freedom of the press, freedom of religion | ||||
| 134. The disagreement between these two men on the role of the national government resulted in the creation of two political parties. | Alexander Hamilton and Thomas Jefferson | ||||
| 135. Alexander Hamilton became the leader of the: | Federalist Party | ||||
| 136. Thomas Jefferson became leader of this party. | Democratic Republicans | ||||
|
137. Which party? – Favored strong national government – Favored limits on states’ powers – Favored development of industry on a national scale – Favored a national bank |
The Federalist Party (led by Hamilton) | ||||
|
138. Which party? – Favored a weak national government – Supported states’ powers – Favored small business and farmers – Opposed a national bank |
The Democratic Republican Party (led by Jefferson) | ||||
| 139. Which party wanted a weak national government and more power with the states? | The Democratic Republicans | ||||
| 140. Which party favored big business and industry, rather than small business and farmers? | The Federalist Party | ||||
| 141. Which party opposed a national bank? | The Democratic Republicans | ||||
| 142. Who were the first five presidents? | George Washington, John Adams, Thomas Jefferson, James Madison, John Monroe | ||||
| 143. All of the first five presidents were Virginians except: | John Adams | ||||
| 144. What were some of George Washington's accomplishments? |
• Federal court system was established. • Political parties grew out of the disagreements between Hamilton and Jefferson over the proper role of the national government. • The Bill of Rights was added to the Constitution. • Plans were initiated for development of the national capital in Washington, D.C |
||||
| 145.Who was an African American astronomer and surveyor that helped complete the design for Washington, D.C.? | Benjamin Banneker, | ||||
| 146. A two-party system emerged during the presidency of: | John Adams | ||||
| 147. What were some of the accomplishments of Jefferson's presidency? |
• He bought Louisiana from France
(Louisiana Purchase). • Lewis and Clark explored this new land west of the Mississippi River |
||||
| 148. During whose presidency, did the War of l812 caused European nations to gain respect for the United States? | James Madison | ||||
| 149. One of Monroe's accomplishments was the: | Monroe Doctrine | ||||
| 150. What does the Monroe Doctrine do? | It warns European nations not to interfere in the Western Hemisphere | ||||
| 151. 1801 and 1861 was a period of: | vast territorial expansion and settlement. | ||||
 152.
What new territories were added to the United States between 1801 and
1861? 152.
What new territories were added to the United States between 1801 and
1861? |
Louisiana Purchase Florida Texas Oregon California |
||||
| 153. The land Jefferson bought from France _____ the size of the United States. | doubled | ||||
| 154. Where did Lewis and Clark explore? | The Louisiana Purchase from the Mississippi River to the Pacific Ocean | ||||
| 155. Spain gave _______ to the United States through a treaty. | Florida | ||||
| 156. This state was added after it became an independent republic. | Texas | ||||
| 157. The _______ Territory was divided by the United States and Great Britain. | Oregon | ||||
| 158.War with Mexico resulted in _______ and the southwest territory becoming part of the United States. | California | ||||
| 159. Westward migration was influenced by: | geography and economic opportunity | ||||
| 160. What factors influenced westward migration? |
• Population growth in the eastern states • Availability of cheap, fertile land • Economic opportunity, e.g., gold (California Gold Rush), logging, farming, freedom (for runaway slaves) • Cheaper and faster transportation, e.g., rivers and canals (Erie Canal), steamboats • Knowledge of overland trails (Oregon and Santa Fe) • Belief in the right of “Manifest Destiny”—The idea that expansion was for the good of the country and was the right of the country |
||||
| 161. The idea that expansion was for the good of the country and was the right of the country is: | Manifest Destiny | ||||
| 162. Prior to the Civil War, most industrialization in America was in the North; however: | the equipment produced in the North had an impact on the farming society in the South. | ||||
| 163. Name 4 inventions that affected the lives of Americans? | Cotton gin, reaper, steamboat, steam locomotive | ||||
| 164. What was the result of the invention of the cotton gin? | It increased the production of cotton and thus increased the need for slave labor to cultivate and pick the cotton. | ||||
| 165. Who invented the cotton gin"? | Eli Whitney | ||||
| 166. What was the result of the invention of the reaper? | The reaper increased the productivity of the American farmer. | ||||
| 167. Who invented the reaper? | Jo Anderson (a slave) and Cyrus McCormick | ||||
| 168. What was the result of the invention of the steamboat? | It provided faster river transportation that connected Southern plantations and farms to Northern industries | ||||
| 169. Who invented the steamboat? | Robert Fulton | ||||
| 170. What was the result of the invention of the steam locomotive? | The steam locomotive provided faster land transportation. | ||||
| 171. People working to end slavery were called: | abolitionists | ||||
| 172. The suffrage movement helped women gain: | equal rights. | ||||
| 173. What did abolitionists demand? | Freeing of the slaves. | ||||
| 174. What did abolitionists believe about slavery? |
Abolitionists believed that slavery was
wrong. – Morally wrong – Cruel and inhumane – A violation of the principles of democracy |
||||
| 175. Name 3 abolitionist leaders. |
– Harriet Tubman – William Lloyd Garrison – Frederick Douglass |
||||
| 176. What were the main ideas expressed during the suffrage movement? |
Supporters believed that women were
deprived of basic rights. – Denied the right to vote – Denied educational opportunities, especially higher education – Denied equal opportunities in business – Limited in rights to own property |
||||
| 177. Name 3 leaders of the suffrage movement. |
– Isabel Sojourner Truth – Susan B. Anthony – Elizabeth Cady Stanton |
||||
| 178. The North and South disagreed over many things, but the biggest issue dividing the nation and leading to the Civil War was: | slavery | ||||
| 179. The North was mainly an _____ society in which people held jobs. | urban | ||||
| 180. The South was primarily an __________ society in which people lived in small villages and on farms and plantations. | agricultural | ||||
| 181. What are tariffs? | Taxes on imported goods | ||||
| 182. Who wanted tariffs, the North or the South? | The North | ||||
| 183. Why did the North want tariffs on imported goods? | To protect factory owners and workers from foreign competition | ||||
| 184. Why did the South oppose tariffs? | Tariffs would cause prices of goods to increase. | ||||
| 185. Another major conflict between the North and South was the issue of states’ rights vs. _____. | strong central government | ||||
| 186. Name 4 issues that divided the North and the South? |
1. slavery; 2. tariffs; 3. cultural differences (urban society vs. agricultural society); 4. states' rights vs. strong central government |
||||
| 187. The North believed that the nation was a union and: | could not be divided. | ||||
| 188. Southerners believed that they had the power to declare any national law _______. | illegal | ||||
| 189. Northerners believed that the national government’s power was: | supreme over that of the states | ||||
| 190. Southerners felt that the abolition of slavery would destroy their region's: | agricultural economy | ||||
| 191. Northerners believed that slavery should be abolished because it was: | morally wrong. | ||||
| 192. Name 3 compromises that attempted to resolve differences over slavery in new states joining the Union. |
Missouri Compromise (1820); Compromise of l850; Kansas-Nebraska Act |
||||
| 193. What was the result of the Missouri Compromise (1820)? | Missouri entered the Union as a slave state; Maine, as a free state. | ||||
| 194. What was the result of the Compromise of l850? | California would be a free state. The Southwest territories would decide about slavery themselves. | ||||
| 195. What was the result of the Kansas-Nebraska Act? | People in these territories would decide the slavery issue by popular vote ("popular sovereignty"). | ||||
| 196. The purpose of the 3 compromises was : | to keep the number of slave and free states equal so neither side would gain control of Congress. | ||||
| 197. What happened after Lincoln became president? | The southern states seceded from the Union | ||||
| 198. What event marked the beginning of the Civil War? | Confederate forces attacked Fort Sumter, in South Carolina | ||||
| 199. Lincoln and many Northerners believed that the United States was one nation that could not be: | separated or divided | ||||
| 200. Most Southerners believed that states had freely created and joined the union, and could therefore: | freely leave it | ||||
| 201. The states that seceded from the Union favored slavery because they were: | dependent upon labor-intensive cash crops | ||||
 Alabama;
Arkansas; Florida; Georgia; Louisiana; Mississippi; North Carolina; South
Carolina; Tennessee; Texas; Virginia Alabama;
Arkansas; Florida; Georgia; Louisiana; Mississippi; North Carolina; South
Carolina; Tennessee; Texas; Virginia202. What did these states do? |
They seceded from the Union | ||||
| 203. Which four slave states stayed in the Union? |
Delaware Kentucky Maryland Missouri |
||||
| 204. The four slave states that stayed in the Union were called: | Border states | ||||
| 205. Western counties of Virginia that refused to secede from the Union formed: | the state of West Virginia | ||||
| 206. During the Civil war, Abraham Lincoln was: | President | ||||
| 207. Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation to: | free the slaves | ||||
| 208. Lincoln was determined to ________, by force if necessary. | preserve the Union | ||||
| 209. Lincoln believed the United States was one nation, not a: | collection of independent states | ||||
| 210. Who wrote the Gettysburg Address? | Lincoln | ||||
| 211. In the Gettysburg Address, Lincoln said that said the Civil War was being fought to preserve a government: | “of the people, by the people, and for the people.” | ||||
| 212. Who was president of the Confederate States of America? | Jefferson Davis | ||||
| 213. Who was general of the Union army that defeated Lee? | Ulysses S. Grant | ||||
| 214. Who was leader of the Army of Northern Virginia? | Robert E. Lee | ||||
| 215. Who was offered command of the Union forces at the beginning of the war but chose not to fight against Virginia? | Robert E. Lee | ||||
| 216. At the end of the war, what did Lee urge Southerners to do? | Lee urged Southerners to accept defeat and reunite as Americans, even though some Southerners wanted to keep fighting. | ||||
| 217. How were Lincoln and Lee's views about the Union the same and how did they differ? | Both wanted to preserve the Union, but Lincoln was willing to do it by force, and Lee did not think the Union should be held together by force. | ||||
| 218. Who was Thomas “Stonewall” Jackson? | A skilled Confederate general from Virginia who played a big role in the First Battle of Bull Run. | ||||
| 219. Who was Frederick Douglass? | A former slave who escaped to the North and became an abolitionist | ||||
| 220. What event began the Civil War? | The firing on Fort Sumter, S.C. | ||||
| 221. What was the first major battle of the Civil War? |
The first Battle of Manassas (Bull Run)
|
||||
| 222. What was an important result of the signing of the Emancipation Proclamation? | It made “freeing the slaves” the new focus of the war. Many freed slaves joined the Union army. | ||||
| 223. What was the result of the Battle of Vicksburg? | The North got control of the Mississippi River. This divided the South in two parts. | ||||
| 224. What battle was considered the turning point of the war? | The Battle of Gettysburg, where the North repelled Lee’s invasion. | ||||
| 225. What happened at Appomattox Court House in 1865? | Lee’s surrender to Grant ended the war | ||||
| 226. Describe life and conditions on the battlefield? | Extremely harsh; many died from disease and exposure. | ||||
| 227. What hardships were experienced during the Civil War? |
· Families and friends were often pitted
against one another. · Disease was a major killer. · Combat was brutal and often man-to-man. |
||||
| 228. What was women's role in the war? | Women were left to run businesses in the North and farms and plantations in the South. | ||||
| 229. Who was the Civil War nurse, who created the American Red Cross? | Clara Barton | ||||
| 230. What was the condition of the South at the end of the war? |
Much of the South was destroyed by the end
of the war. Richmond and Atlanta had were burned Confederate money was worthless. |
||||
| 231. What was the role of African Americans in the Civil War? | They fought in both the Confederate and Union armies. | ||||
| 232. How were African American Soldiers treated? |
• African American soldiers were paid less
than white soldiers. • African American soldiers were discriminated against and served in segregated units under the command of white officers. |
||||
| 233. A brave and heroic African American sailor and later a Union naval captain who became a Congressman after the Civil War was: | Robert Smalls | ||||
| 234. Which amendments were added to the Constitution after the war to address the issues of slavery and guarantee equal protection under the law for all citizens? | The 13th, 14th, and 15th Amendments | ||||
| 235. Which amendment banned slavery? | The 13th Amendment | ||||
| 236. Which amendment granted citizenship to all persons born in the United States and guaranteed them equal protection under the law? | The 14th Amendment | ||||
| 237. Which amendment insured all citizens the right to vote regardless of race or color or previous condition of servitude? | The 15th Amendment | ||||
| 238. What do the 13th, 14th, and 15th amendments do? | They guarantee equal protection under the law for all citizens. | ||||
| 239. The period after the Civil War is called: | Reconstruction | ||||
| 240. What were some Reconstruction policies? |
-Northern soldiers supervised the South and
Southern military leaders could not hold office. -African Americans gained equal rights and some held public office. |
||||
| 241, What was the purpose of Civil Rights Act of 1866? | It gave equal rights to African Americans | ||||
| 242. What were some of the problems created by Reconstruction policies? |
-The Reconstruction policies were harsh and
created resentment. -Southerners resented northern “carpetbaggers" |
||||