|
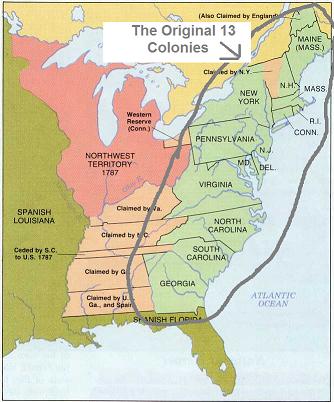
STANDARD US1.3a,b
American Indians |
In which
areas did the American Indians (First Americans) live?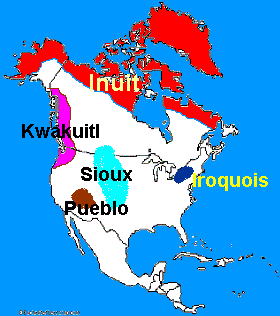
Prior to the arrival of Europeans, American Indians (First Americans)
were dispersed across different environments in North America.
Inuit inhabited present-day Alaska and
northern Canada. They lived in Arctic areas where the temperature is below
freezing much of the year.
Kwakiutl inhabited the Pacific Northwest
coast, characterized by a rainy, mild climate.
Sioux inhabited the interior of the
United States, called the Great Plains and characterized by dry grasslands.
Pueblo inhabited the Southwest in
present-day New Mexico and Arizona, where they lived in desert areas and
areas bordering cliffs and mountains.
Iroquois inhabited northeast North
America, the Eastern Woodland, which is heavily forested.
How did geography and climate affect the way American Indian (First
American) groups met their basic needs?
The American Indians (First Americans) fished, hunted, and harvested crops
for food. Clothing was made from animal skins and plants. Their shelter was
made of resources found in their environment (e.g., sod, stones, animal
skins, wood). |
|
STANDARD US1.5b,c,d Life in the New England,
Mid-Atlantic, and Southern colonies |
|
*How did climate and
geographic features distinguish the three regions from
each other?
*How did people use the natural resources of their
region to earn a living?
*How did political and social life evolve in each of
the three regions?
|
| New
England |
Mid-Atlantic |
South |
Geography and climate
Appalachian Mountains, Boston harbor, hilly terrain,
rocky soil, jagged coastline
Moderate summers, cold winters |
Geography and climate
Appalachian Mountains, coastal lowlands (harbors and
bays, wide and deep rivers), rich farmlands
Moderate climate |
Geography and climate
Appalachian Mountains, Piedmont, Atlantic Coastal
Plain, good harbors, rivers
Humid climate |
Economy
Fishing, shipbuilding industry and naval supplies,
trade and port cities
Skilled craftsmen, shopkeepers |
Economy
Livestock and grain, trading
Unskilled and skilled workers and fishermen |
Economy
Large farms/plantations, cash crops, wood products,
small farms
Slavery |
Social
life
Village and church as center of life
Religious reformers and separatists
|
Social
life
Villages and cities
Varied and diverse lifestyles
Diverse religions |
Social
life
Plantations (slavery), mansions, indentured servants,
few cities, few schools
Church of England |
Political and civic life
Town meetings |
Political and civic life
Market towns |
Political and civic life
Counties |
How did
peoples lives vary among different social groups in
colonial America?
The colonies were
made up of different groups of people whose lives
varied depending on their social position. |
Large landowners
Lived predominately in the South
Relied on indentured servants and/or slaves for labor
Were educated in some cases
Had rich social culture |
Farmers
Worked the land according to the region
Relied on family members for labor |
Artisans
Worked as craftsmen in towns and on the plantation
Lived in small villages and cities |
Women
Worked as caretakers, house-workers, homemakers
Could not vote
Had few chances for an education |
Indentured servants
Consisted of men and women who did not have money for
passage to the colonies and who agreed to work without
pay for the person who paid for their passage
Were free at the end of their contract |
Slaves
Were captured in their native Africa and sold to
slave traders, then were shipped to the colonies where
they were sold into slavery
Were owned as property for life with no rights
Were often born into slavery (Children of slaves were
born into slavery.) |
|
How did England impose its
political and economic control over the colonies?
England established and attempted to maintain
control over the colonies.
Economic relationships
England imposed strict control over trade.
England taxed the colonies after the French and
Indian War.
Colonies traded raw materials for goods.
Political relationships
Colonists had to obey English laws that were enforced
by governors.
Colonial governors were appointed by the king or by
the proprietor.
Colonial legislatures made laws for each colony and
were monitored by colonial governors. |
|
STANDARD US1.6a
Dissatisfaction leads to Revolution |
What steps did
England take to increase control over its colonies?
Why did many colonists become dissatisfied with
Englands control over the colonies?
As England expanded control over the American
colonies, many colonists became dissatisfied and
rebellious.
Englands reasons for control
England desired to remain a world power.
England imposed taxes, such as the Stamp Act, to
raise necessary revenue to pay the cost of the French
and Indian War.
Englands reasons for taxation
To help finance the French and Indian War
To help with the maintaining of English troops in the
colonies
Sources of colonial dissatisfaction
Colonies had no representation in Parliament.
Some colonists resented power of colonial governors.
England wanted strict control over colonial
legislatures.
Colonies opposed taxes.
The Proclamation of l763 hampered the western
movement of settlers. |
|
STANDARD US1.6b
Dissatisfaction Leads to Revolution |
What
ideas/philosophies about government were expressed in
the Declaration of Independence?
New political ideas led to a
desire for independence and democratic government in
the American colonies.
The Declaration of Independence
proclaimed independence from England. It stated that
people have natural (inherent) rights to life, liberty,
and the pursuit of happiness.
Ideas of John Locke
People have natural rights to life, liberty, and
property.
Government is created to protect the rights of people
and has only the limited and specific powers the people
consent to give it.
Key philosophies in the Declaration of Independence
People have certain unalienable rights (rights that
cannot be taken away)life, liberty, pursuit of
happiness.
People establish government to protect those rights.
Government derives power from the people.
People have a right and a duty to change a government
that violates their rights. |
|
STANDARD US1.8a
Westward Expansion |
What new territories became part of the
United States between 1801 and 1861?
Between 1801 and 1861, exploration was encouraged as America
underwent vast territorial expansion and settlement.
New territories added to the United States after 1801
Louisiana Purchase
Jefferson bought land from France (the Louisiana Purchase), which doubled
the size of the United States.
In the Lewis and Clark expedition, Meriwether Lewis and William Clark
explored the Louisiana Purchase from the Mississippi River to the Pacific
Ocean.
Florida
Spain gave Florida to the United States through a treaty.
Texas
Texas was added after it became an independent republic.
Oregon
The Oregon Territory was divided by the United States and Great Britain.
California
War with Mexico resulted in California and the southwest territory
becoming part of the United States. |
|
STANDARD US1.8b Westward Expansion -
Geographic and Economic Factors |
What factors influenced westward
migration?
Westward migration was influenced by geography and
economic opportunity
Geographic and economic factors that influenced westward movement
Population growth in the eastern states
Availability of cheap, fertile land
Economic opportunity, e.g., gold (California Gold Rush), logging,
farming, freedom (for runaway slaves)
Cheaper and faster transportation, e.g., rivers and canals (Erie
Canal), steamboats
Knowledge of overland trails (Oregon and Santa Fe)
Belief in the right of Manifest DestinyThe idea that expansion
was for the good of the country and was the right of the country |
|
STANDARD US1.8c Impact of
Inventions |
How did the inventions affect the lives of Americans?
Prior to the Civil
War, most industrialization in America was in the North; however, the
equipment produced in the North had an impact on the farming society in the
South.
New technologies
The cotton gin was invented by Eli Whitney.
It increased the production of cotton and thus increased the need for slave
labor to cultivate and pick the cotton.
Jo Anderson (a slave) and Cyrus McCormick worked to invent the
reaper. The reaper increased the productivity of the
American farmer.
The steamboat was invented by Robert Fulton.
It provided faster river transportation that connected Southern plantations
and farms to Northern industries.
The steam locomotive provided faster land
transportation. |
|
STANDARD US1.9a Issues
Dividing the Nation |
The student will
demonstrate knowledge of the causes, major events, and effects of the Civil
War by
a) describing the cultural, economic, and constitutional issues that divided
the nation. |
How did cultural, economical,
and constitutional issues create bitter divisions between the North and the
South?
Cultural, economic, and constitutional differences
between the North and the South eventually resulted in the Civil War.
Issues that divided the nation
Slavery
While there were several differences between the North and the South, the
issues related to slavery increasingly divided the nation and led to the
Civil War.
Cultural
The North was mainly an urban society in which people held jobs.
The South was primarily an agricultural society in which people lived in
small villages and on farms and plantations.
Because of their cultural differences, people of the North and South found
it difficult to agree on social and political issues.
Economic
The North was a manufacturing region, and its people favored tariffs that
protected factory owners and workers from foreign competition.
Southerners opposed tariffs that would cause prices of manufactured goods
to increase. Planters were also concerned that England might stop buying
cotton from the South if tariffs were added.
Constitutional
A major conflict was states rights versus strong central government. |
|
STANDARD US1.9b States' Rights and
Slavery |
The student will
demonstrate knowledge of the causes, major events, and effects of the Civil
War by
b) explaining how the issues of states rights and slavery increased
sectional tensions. |
How did the issues of states
rights and slavery increase sectional tension between the North and South?
The South feared that the North would take control
of Congress, and Southerners began to proclaim states rights as a means of
self-protection.
The North believed that the nation was a union and could not be divided.
While the Civil War did not begin as a war to abolish slavery, issues
surrounding slavery deeply divided the nation.
Issues that divided the nation
An important issue separating the country related to the power of the
Federal government. Southerners believed that they had the power to declare
any national law illegal. Northerners believed that the national
governments power was supreme over that of the states.
Southerners felt that the abolition of slavery would destroy their
regions economy. Northerners believed that slavery should be abolished for
moral reasons.
Compromises attempting to resolve differences
Missouri Compromise (1820): Missouri was a slave state; Maine, a
free state.
Compromise of l850: California was a free state. Southwest
territories would decide about slavery.
Kansas-Nebraska Act: People decided the slavery issue (popular
sovereignty).
Southern secession
Following Lincolns election, the southern states seceded from the Union.
Confederate forces attacked Fort Sumter, in South Carolina, marking the
beginning of the Civil War.
Lincoln and many Northerners believed that the United States was one nation
that could not be separated or divided. Most Southerners believed that
states had freely created and joined the union and could freely leave it. |
|
STANDARD US1.9c South Secedes |
 |
Southern states that were
dependent upon labor-intensive cash crops seceded from the Union.
Northernmost slave states (border states) stayed in the Union.
Which states seceded from the Union?
States that seceded from the Union
Alabama
Arkansas
Florida
Georgia
Louisiana
Mississippi
North Carolina
South Carolina
Tennessee
Texas
Virginia
|
Which four slave states stayed in the
Union?
States remaining in the Union
Border states (slave states)
Delaware
Kentucky
Maryland
Missouri
Where were the other states that remained in the Union located?
Free States
California
Connecticut
Illinois
Indiana
Iowa
Kansas
Maine
Massachusetts
Michigan
Minnesota
New Hampshire
New Jersey
New York
Ohio
Oregon
Pennsylvania
Rhode Island
Vermont
West Virginia (Western counties of Virginia that refused to secede from
the Union)
Wisconsin |
|
STANDARD US1.10a The 13th, 14th, and
15th Amendments |
What are the basic provisions of the
13th, 14th, and 15th Amendments?
The 13th, 14th, and 15th Amendments address the issues of slavery and
guarantee equal protection under the law for all citizens.Basic
provisions of the Amendments
13th Amendment: Bans slavery in the United States and any of
its territories
14th Amendment: Grants citizenship to all persons born in
the United States and guarantees them equal protection under the law
15th Amendment: Ensures all citizens the right to vote
regardless of race or color or previous condition of servitude
These three amendments guarantee equal protection under the law for
all citizens. |
|
STANDARD US1.10b
Effects of Reconstruction on the South |
What were the Reconstruction policies for
the South?
The Reconstruction policies were harsh and created problems in the
South.
Reconstruction attempted to give meaning to the freedom that the former
slaves had achieved.
Reconstruction policies and problems
Southern military leaders could not hold office.
Southerners resented northern carpetbaggers, who took advantage of the
South during Reconstruction.
African Americans held public office.
African Americans gained equal rights as a result of the Civil Rights Act
of 1866, which authorized the use of federal troops for its enforcement.
Northern soldiers supervised the South. |